Neural tube defects (NTD) are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord and these happen in the first month of pregnancy; even before a woman discovers that she is pregnant.
Neural tube defects (NTD) are birth defects of the brain and spinal cord and these happen in the first month of pregnancy; even before a woman discovers that she is pregnant. Basically, what starts out as a tiny, flat ribbon, turns into a tube by the end of the first month of pregnancy. And, later as the embryo develops, the neural tube too begins to change into a complicated structure of bones, tissue and nerves that eventually forms the spine and nervous system of the child. So, technically, in children born with NTD, something goes wrong with the development of the neural tube and the spinal column doesn’t close completely. Therefore, NTDs often pose a serious threat to the babies, including death in some extreme cases.
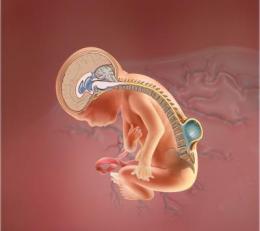
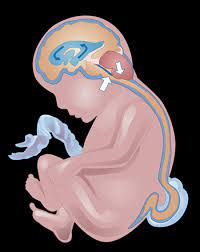
Neural tube defects include spina bifida, anencephaly, occult spinal dysraphism and encephalocele. However, the two most common types are spina bifida and anencephaly.
Spina bifida: It is the most common NTD. During this condition, the tiny bones of the vertebrae do not close completely, and a part of the spinal cord pokes through the spine.
Spina bifida sometimes can be treated surgically before or after the child birth. And children born with this condition may have paralysed legs or problems controlling their bladder and bowel.
Anencephaly: It is one of the most severe NTDs as babies born with this condition do not have fully developed brain, skull and scalp. Babies with anencephaly are usually either stillborn or die shortly after birth.
The condition occurs when the upper part of the neural tube that forms the brain does not close completely. Also, girls are three times more likely to be born with anencephaly than boys.
Encephalocele: This is another form of NTD but it is a rare condition that affects the brain and skull of a new born child. In this defect, a sac that contains the membranes to cover the brain pokes through an opening in the skull. Often, part of the brain pokes through, too. The most common site for this condition is at the base of the skull where it meets the neck, or between the forehead and nose or in middle of the upper part of the skull.
Babies with encephalocele need a surgery so as to close the opening and place parts of the brain back inside the skull. At least half of all children with encephalocele have other birth defects too. These could be intellectual disabilities, movement problems or paralysis, vision problems and seizures. They may have inborn defects of the head and face too.
Also, sometimes babies are born with the condition called hydrocephalus, in which there’s a build-up of cerebrospinal fluid in the skull. The condition causes the brain to swell and it leads to a large spectrum of developmental, physical, and intellectual impairments. Therefore, babies born with this defect are treated surgically through shunt insertion. The shunt is a drainage system made of a tube with a valve through which excess fluid is drained out either into the child’s chest or abdominal cavity. A shunt implant runs under the skin and is typically permanent and has to be monitored regularly.
Causes
Though the exact cause of NTD is unknown, however, there may be one or several causes responsible. These may include:
* Genetic reason, which means a baby inherits the condition from either of his parents.
* Women who take certain anti-seizure medications.
* Women who are obese.
* Women who have diabetes.
Prevention and Cure
Neural tube defects can easily be prevented if women who plan to conceive have enough Vitamin B folic acid (folate) before and during the first 3 months of pregnancy. Adequate folate levels are critical during the early days of the developing embryo because it is during this period that the neural tube defect occurs. Also, because most women do not realise that they are pregnant, especially during unplanned pregnancies, it is important that all women of childbearing age ensure that they consume sufficient dose of folate or folic acid.
And, women who have already had a pregnancy affected by an NTD, are at a greater risk, therefore, they need even more dosage of folic acid.
Screening
Parental screening tests during pregnancy often help to identify if the foetus is at increased risk of having an NTD. These screening tests include blood test, ultrasound of baby’s skull and spine and amniocentesis, if the screening test shows risk of NTD.
Management and Treatment
* Children affected with NTD may require multidisciplinary treatments so as to address any physical, developmental, hearing, and visual difficulties that may occur with respect to their condition.
* Open NTDs need immediate attention and hence these should be closed promptly.
* Hydrocephalus can be treated through shunt insertion.
* Symptomatic Chiari malformations are to be treated through suboccipital craniotomy and decompression of the posterior fossa and tonsils.
* Syrinx, or a fluid-filled cavity within the spinal cord or brainstem are treated with laminectomy and placement of a syringosubarachnoid stent to divert the CSF out of the central canal.
Tuberculosis of Spine
The spine is the most dangerous site for skeletal tuberculosis and it accounts for approximately half of all cases of musculoskeletal TB. Though commonly seen among children and young adults, spinal TB, also called “Pott’s” disease, usually affects the thoracic part of the spine and is the most destructive form of tuberculosis. Also, unlike TB of lungs, patients with spinal TB are generally not contagious because TB spreads through coughed up active virus particles and these patients with spinal TB do not suffer from coughing. Which is why they fail to suspect that they have or could ever have tuberculosis.
Spinal TB usually takes two forms: In the first scenario, the patient’s general symptoms are mild. The infection usually starts in the anterior part of a disc, and spreads to the adjacent surface of the body of a vertebra, or to two adjacent ones. It seldom involves his neural arches. With the result, as his vertebrae collapse, his spine angles forwards to produce a kyphus (an increase in the normal convex curve of the spine). The shape of an individual’s spinal deformity depends on how many of his vertebrae are diseased.
In the second form, the patient shows symptoms which are more severe as several of his vertebrae are involved (including some in his neck), and his disc spaces may not be narrowed. One of his many symptoms would be pain in his back, and increasing kyphosis. Later, pus from his diseased vertebrae may track along tissue planes to present as a cold abscess in unexpected places, particularly in his groin (psoas abscess). Resultantly, an individual may become paraplegic.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Patients with spinal TB may or may not exhibit generalised signs of tuberculosis such as fever, fatigue, night sweats and unexplained weight loss. Howevere, it causes constant and unbearable back pain as the virus degrades the discs cushioning the vertebrae.
Spine and skeletal TB can be diagnosed with the help of CT Scans and MRI reports. It is severe because if not detected and treated in time, the disease can cause paralysis which may take years to get cured.
Treatment
Spinal tuberculosis is destructive as it can spread from one vertebra to the next, thereby weakening the bones and destroying the cushioning discs between them. In severe cases, the spine can collapse and compress the spinal cord, causing paralysis of the lower body. And if spinal TB progresses to destruction of the vertebrae and discs, the bones of the spine jut forward and form a hump.
The treatment and management of spinal TB may depend on how early it has been diagnosed. However, in its early stages medication course is prescribed to the patients and if there is any kind of fluid or pus formation, it is extracted out through Aspiration. Extreme case of Spine TB may even lead to major destruction of bone or cause paralysis in a few cases. The treatment and recovery time depends if paralysis is mild, moderate or severe, accordingly the patient is advised to undergo spinal fusion surgery to decompress or fix the spine.
Copyright © 2020. All Rights Reserved.
Designed and Developed by Easy Solution 360